Sale!
Sale!
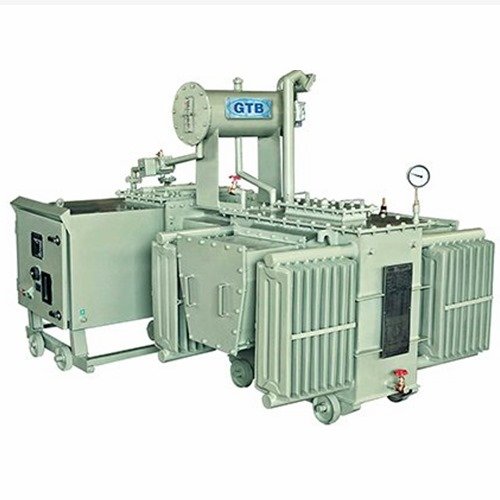


Transformers
₹ 0.00